The Disappearance of the Kelp Forest
Salt Point State Park and the Marine Ecosystem
Outline Link to heading
Introduction Link to heading
Our project captures the loss of the kelp forest at Salt Point State Park, influenced by the disease-stricken populations of the Sunflower Sea Star, the sudden marine heat waves due to global warming and El Niño, and the overhunting of sea otters. The goal is to show the transformation from a healthy marine ecosystem to an urchin barren through three simple visualizations built with Blender, with each model capturing one of three stages. We were inspired to present this topic from a personal engagement with a park ranger during a visit to Salt Point State Park.
A Healthy Forest Link to heading
The first model depicts a healthy and balanced marine ecosystem that existed before 2010. As shown by the model, the ecosystem had several species of plants and animals, indicating high biodiversity. The kelp forest was also home to other small fish, mollusks, and crustaceans that were not captured in the model, which made the coast of Salt Point State Park a feeding ground for larger creatures, mainly seals, sea lions, and whales.

Immediate Impacts Link to heading
Next, the second model shows the immediate impact of sudden marine heat waves, influenced by global warming and El Nino. This caused coral bleaching, kelp nutrient deficits, and sea star wasting syndrome, a bacteria infection that spread quickly through the sunflower sea star population, a natural sea urchin predator. This created a catastrophic disturbance in the ecosystem.

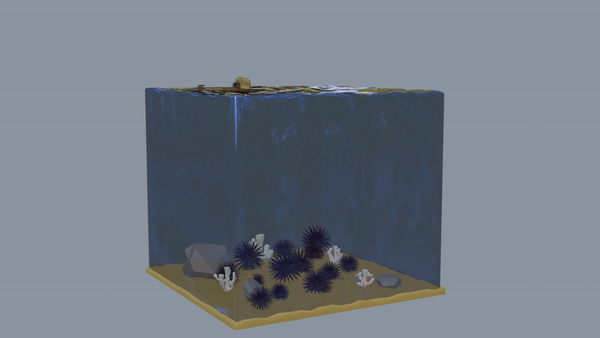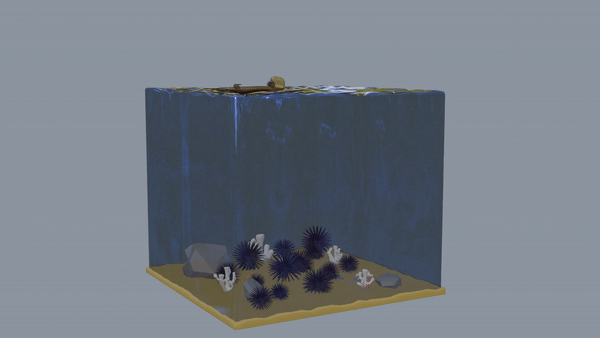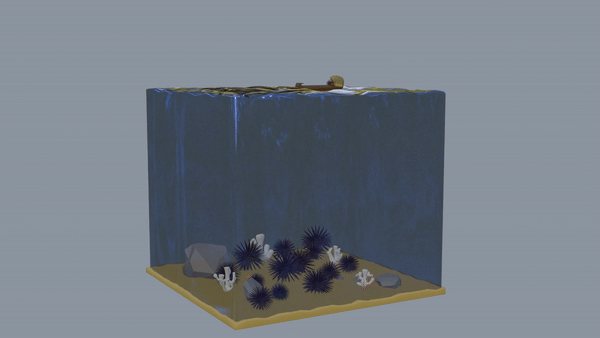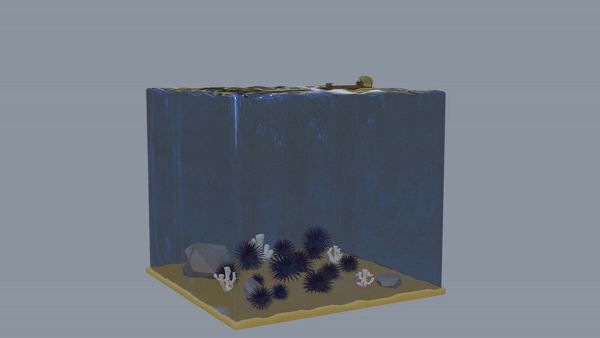
Urchin Barren Link to heading
Finally, the last model shows an “urchin barren”, where the kelp forest has turned into a wasteland due to uncontrolled sea urchin populations. Unfortunately, neither the sunflower sea star population nor the otter population have rebounded enough to control the urchin population, making it extremely difficult for the kelp forest to rejuvenate. This has also caused a drastic decrease in biodiversity at Salt Point State Park’s marine ecosystem as smaller creatures can no longer thrive.
Takeaway Link to heading
The death of the kelp forest and the cascading effects on the rest of the marine ecosystem at Salt Point State Park serve as an important warning about how anthropogenic impacts on the environment must be carefully monitored and controlled. As covered by the course, many ecosystem services and resources that we use are provided for by a healthy ocean, and therefore, we must be more proactive in marine conservation.
Acknowledgements Link to heading
This project was conducted with Cameron Dang during the 2024 Fall Semester of ESPM 198 (Scuba and Marine Conservation) at UC Berkeley through the College of Environmental Science, Policy, and Management. This was a student-led course under DECALS.